The durability and safety of equipment hinge significantly on the quality of abrasion-resistant sleeves. Therefore, identifying the raw material composition of these sleeves is crucial. To aid in your understanding and selection of wear-resistant sleeving, this article outlines two commonly employed testing methods: the water-floating test and the burning test.
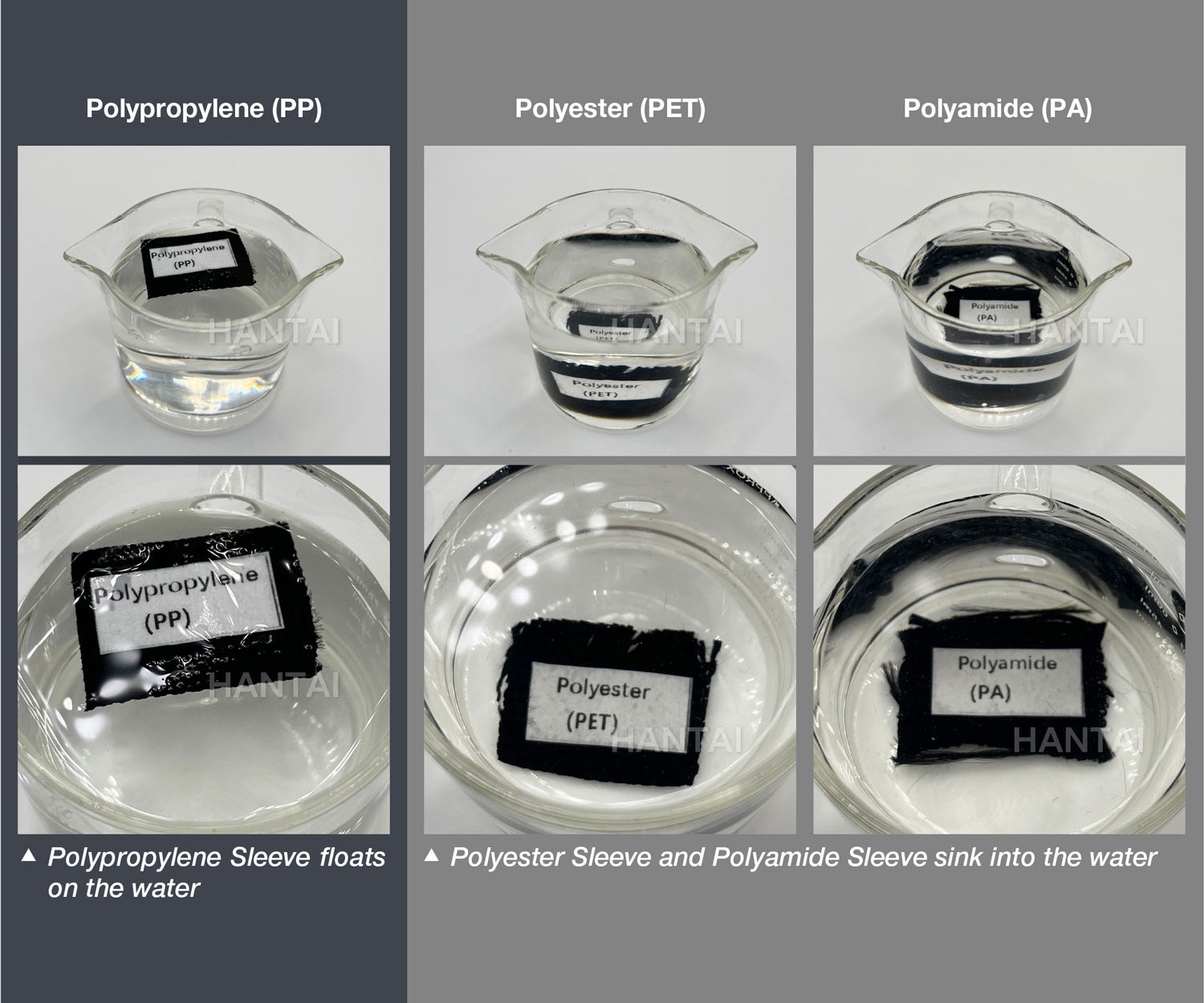
A. Water-Floating Test
•Polypropylene protective sleeves tend to float on water.
•Polyester and polyamide protective sleeves, on the other hand, sink into the water.
B. Burning Test
•Polyamide protective sleeves produce white smoke with a pungent odor.
•Polyester and polypropylene protective sleeves emit black smoke without a pungent smell.
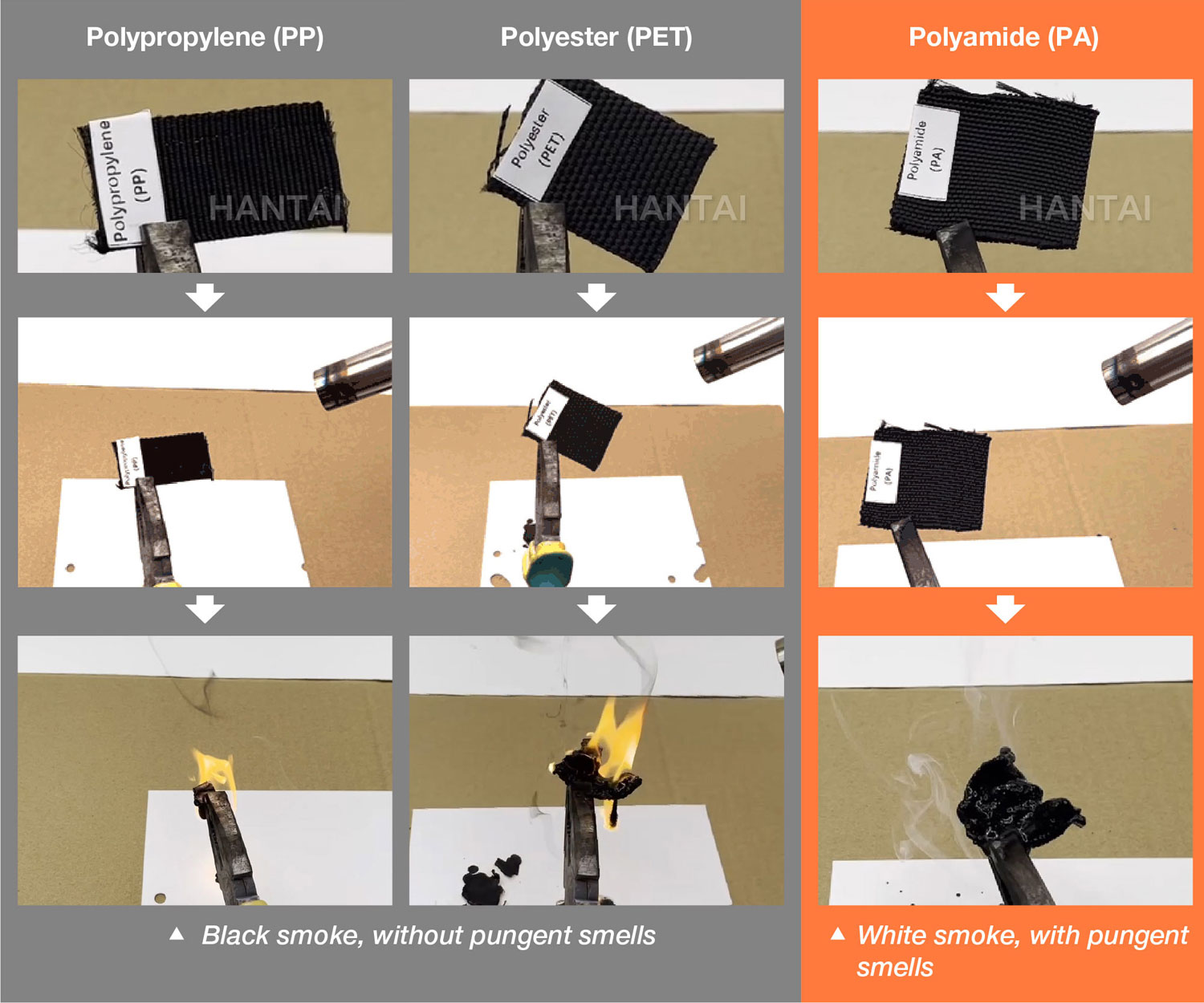
Furthermore, it has been observed that abrasion-resistant sleeves of superior quality, such as polyester and polyamide sleeves, tend to leave brighter burning residues. Conversely, polypropylene sleeves leave a relatively dull residue upon burning.






